Keyfactor is thrilled to announce a new partnership with Symmera, a leader in enterprise digitalization. Together, Symmera and Keyfactor provide holistic digital trust for connected devices and edge solutions based on open standards.
The IT and OT markets continue to become more intelligent and utilize more AI and machine learning. Manufacturers and end users now face a host of challenges in balancing security, scalability, availability, and interoperability while trying to maintain simplicity of implementation.
While security by design is essential, cybersecurity extends across the entire product...
A New Era for Cyber Resilience
As we welcome and celebrate the beginning of a new year, and the end of the first quarter of the 21st century, does a new era for cyber resilience appear elusive? What will change in the next quarter of this century?
Episodes of payment card fraud, compromised credentials, corporate data breaches, phishing emails, SMS spam, and ransomware targeting institutions and consumers will inevitably, and yet again, become headline news in the weeks and months ahead. The professional hackers and cybercrime syndicates have made significant advancements with ingenuity to break security countermeasures with...
Cyber Resilience for Critical Infrastructure
Over the past decade, the cybersecurity industry has tried to solve an operational technology (OT) problem on devices with an information technology (IT) solution on the network. The wiring closet with IT-OT convergence is complex plumbing. The weaknesses and vulnerabilities on OT devices must be addressed head-on by the suppliers with device and application security by design. The attack surface on autonomous and distributed cyber physical systems behooves a risk model based assessment of exposures and countermeasures.
The emerging standards for protection of critical infrastructures and cyber...
The AI Act and Implications for IoT/IIoT Initiatives
The Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act, approved by European Union member states, lawmakers, and the European Commission, went into effect on August 1, 2024. This undoubtedly will have a significant and enduring effect on how data is classified and labelled for acceptance or rejection by AI based machine learning (ML) and deep-learning (DL) applications and services. Today these implementations implicitly trust the accuracy and authenticity of massive training datasets (e.g., metrics, text, image, audio, video) to fine-tune billions of model parameters. Programmatically differentiating deep-fake...
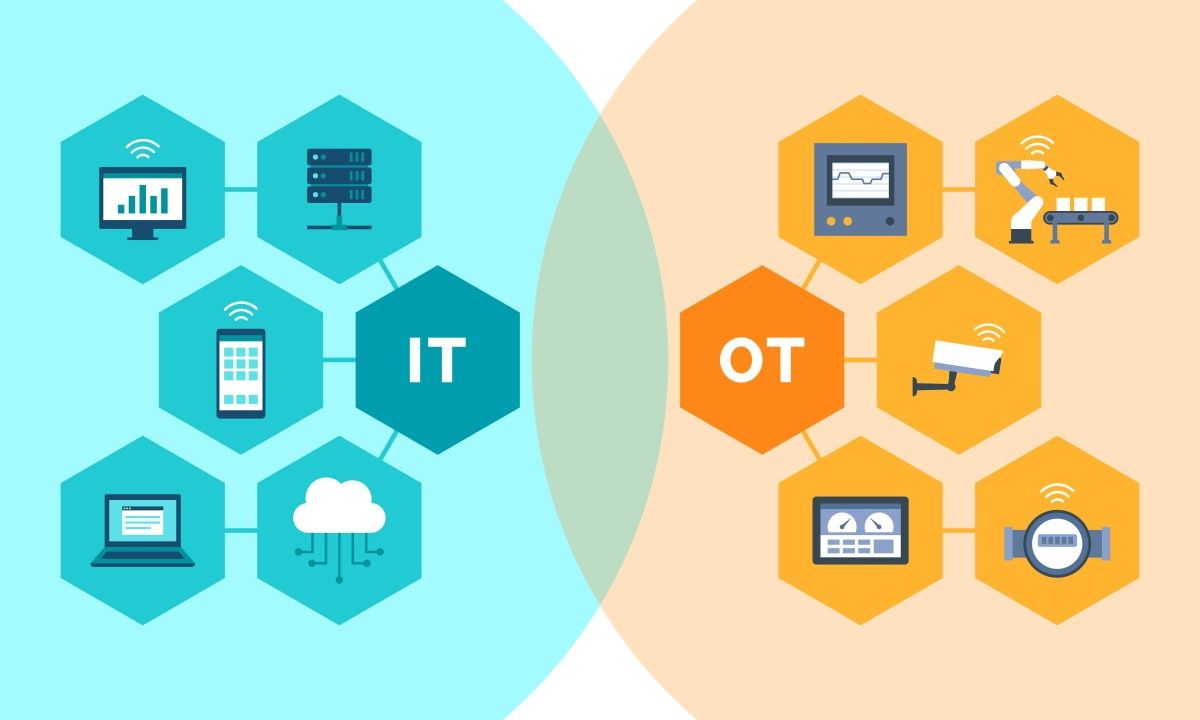
The IT-OT Dichotomy and Passage to Digitalization
The difference between information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) must be viewed from the perspective of visibility, control, and lifecycle orchestration. While these viewpoints may appear to be trivial the inherent dichotomy between IT and OT is profound.
It is not what has “not changed” but what “has changed” that has caused the IT-OT divergence problem to begin with. IT-OT systems have coexisted for many decades across industry segments, however, what has evolved are the requirements for visibility and control of cyber-enabled devices driven by threat...
The Sherpa Guide to Keys and Certificates
When it comes to salesmanship, the quintessential difference between computer salesmen and car salesmen is that the car salesmen know when they are lying. The stakeholder’s assessment of whether to use asymmetric or symmetric keys, public key infrastructure (PKI) or PKI-less platforms, thick agent-based (intricate key and certificate management protocols, aftermarket third-party applications) or thin agent-less (low coding, simplified polyglot APIs) solutions to manage and protect devices in the emerging era of Extended Internet of Things (XIoT) is a critical decision point. Enterprise Digitalization...
Cyber Proofing Devices and Data
Over the past decades it became evident that compromise of user and service accounts could play a major factor in high profile cyberattacks, ransomware and data breaches. Through compromise of user credentials, unauthorized access could be obtained to infiltrate networks, install malware (from exploits to viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, ransomware, rootkits, and bootkits), and infect computer systems for nefarious purposes. That led to server and data enclaves within Enterprise data centers under the surveillance of network and service operations center (NOC/SOC) administrators and operators....
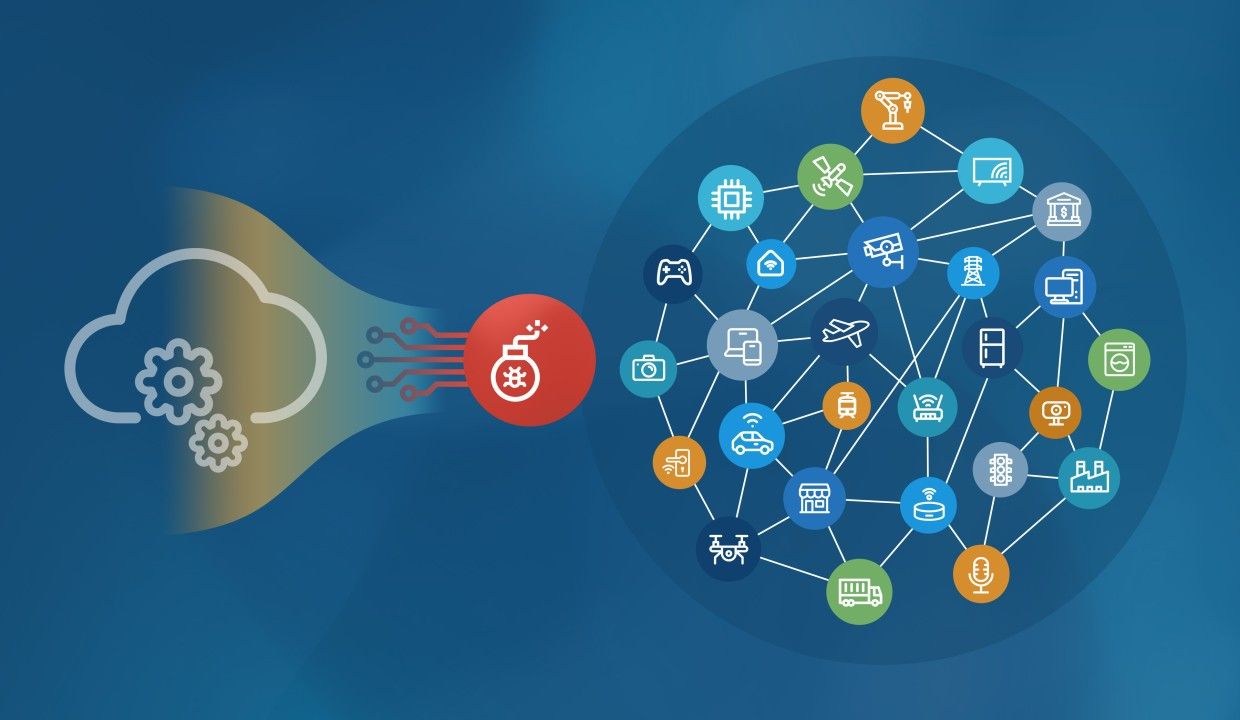
Cyber Attacks on Devices in the AI-ML Era
Any offensive advance in a conventional war requires taking down ground defenses with air power before launching a ground invasion. In the early days of building cybersecurity fortresses the strategic multi-layer defense initiatives comprised of meticulously designed heterogeneous and redundant security countermeasures for intrusion detection and prevention. The evolution thereon was guided by the paradigm of proactive rather than reactive security controls based on reliable real-time threat intelligence feeds, regular expressions, and context-sensitive grammar for deep-packet inspection and...
The Moral Imperative of Artificial Intelligence
Historically, human society has evolved by turning the wheels, and adding the axles, before tightening the grip on the steering wheel.
The lurking perils of artificial intelligence
While artificial intelligence (AI) offers definitive benefits, it behooves us to consider the unintended negative consequences of human innovations. AI is a dual-use technology that can be repurposed for nefarious use by state actors and digital crime syndicates. The line between deep-learning and deep-fake is treacherously thin. There may be numerical probabilities and likelihoods in mathematics, but there also...